It is funded by a 2% tax levy on all taxpayers, an additional 1% levy on high income earners, in addition to basic income. The private health system is funded by a variety of private medical insurance companies. The largest of these is Medibank Private Limited, which was, till 2014, a government-owned entity, when it was privatized and listed on the Australian Stock Exchange. Australian health funds can be either 'for profit' including Bupa and nib; 'shared' including Australian Unity; or 'non-profit' including GMHBA, HCF Helpful resources and the HBF Medical Insurance. Some, such as Cops Health, have membership limited to specific groups, but the majority have open membership.
These contrast sites run on a commission-basis by contract with their getting involved health funds. The Private Health Insurance Ombudsman also runs a free website that permits consumers to look for and compare personal health insurers' items, which consists of information on price and level of cover. How much is car insurance. Most aspects of personal medical insurance in Australia are managed by the Private Health Insurance http://connergrxi443.lowescouponn.com/more-about-what-is-life-insurance Coverage Act 2007. Problems and reporting of the private health market is performed by an independent government firm, the Private Health Insurance Ombudsman. The ombudsman releases a yearly report that details the number and nature of problems per health fund compared to their market share The private health system in Australia runs on a "neighborhood rating" basis, whereby premiums do not differ exclusively since of a person's previous medical history, current state of health, or (generally speaking) their age (however see Life time Health Cover listed below). Personal medical insurance does not usually cover emergency treatment but subsequent recovery could be paid for if the patient were moved into Check out here a personal patient system. On the 1st of August, 2018 the DHHS released a final rule that made federal changes to Short-Term, Limited-Duration Medical Insurance (STLDI) which lengthened the optimum agreement term to 364 days and renewal for as much as 36 months. This brand-new rule, in combination with the expiration of the penalty for the Individual Required of the Affordable Care Act, has been the subject of independent analysis. The United States health care system relies heavily on private health insurance coverage, which is the primary source of protection for most Americans.
9% of American grownups had private medical insurance, according to The Center for Illness Control and Avoidance. The Agency for Health Care Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that in 2011, personal insurance coverage was billed for 12. 2 million U.S. inpatient hospital stays and sustained around $112. 5 billion in aggregate inpatient healthcare facility expenses (29% of the total nationwide aggregate expenses). Public programs provide the primary source of coverage for a lot of senior people and for low-income kids and households who meet specific eligibility requirements. The main public programs are Medicare, a federal social insurance coverage program for elders and certain disabled people; and Medicaid, moneyed collectively by the federal government and states but administered at the state level, which covers particular very low income kids and their families.
SCHIP is a federal-state partnership that serves certain kids and families who do not receive Medicaid but who can not pay for personal coverage. Other public programs include military health benefits offered through TRICARE and the Veterans Health Administration and benefits supplied through the Indian Health Service. Some states have additional programs for low-income individuals (How much is pet insurance). In the late 1990s and early 2000s, health advocacy business began to appear to help patients handle the intricacies of the health care system. The intricacy of the healthcare system has actually led to a range of issues for the American public. A study discovered that 62 percent of individuals declaring personal bankruptcy in 2007 had unpaid medical expenses of $1000 or more, and in 92% of these cases the medical financial obligations surpassed $5000.
The Medicare and Medicaid programs were approximated to soon account for 50 percent of all nationwide health costs. These factors and numerous others sustained interest in an overhaul of the healthcare system in the United States. In 2010 President Obama signed into law the Client Defense and Affordable Care Act. This Act includes an 'individual mandate' that every American should have medical insurance (or pay a fine). Health policy specialists such as David Cutler and Jonathan Gruber, in addition to the American medical insurance coverage lobby group America's Health Insurance coverage Plans, argued this arrangement was needed in order to offer "ensured issue" and a "neighborhood ranking," which resolve out of favor features of America's health insurance coverage system such as premium weightings, exclusions for pre-existing conditions, and the pre-screening of insurance candidates.
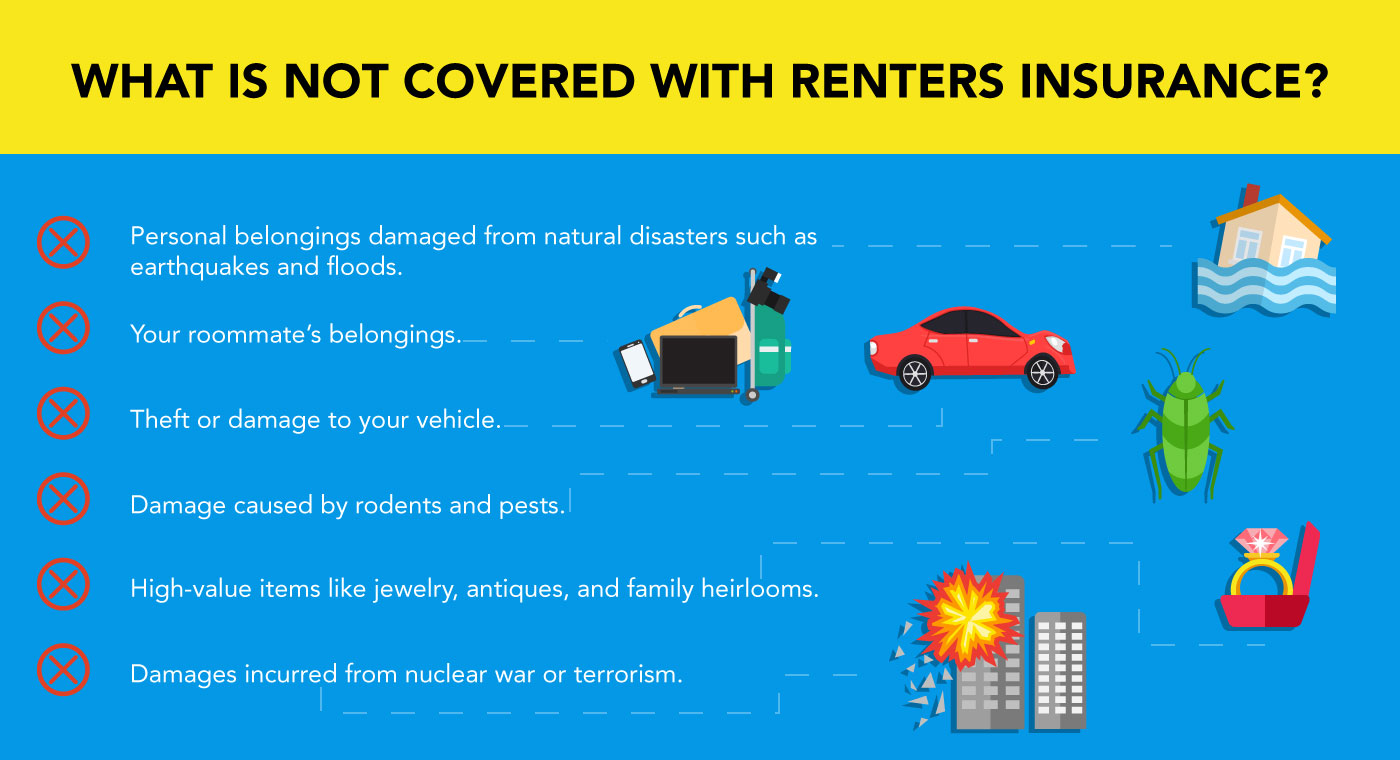
The Basic Principles Of How To Lower Car Insurance
The Patient Defense and Affordable Care Act was identified to be constitutional on 28 June 2012. The Supreme Court figured out that Congress had the authority to use the specific mandate within its taxing powers. In the late 19th century, "accident insurance coverage" started to be readily available, which ran much like modern special needs insurance. This payment design continued up until the start of the 20th century in some jurisdictions (like California), where all laws regulating medical insurance really described impairment insurance. Mishap insurance was first used in the United States by the Franklin Health Guarantee Company of Massachusetts. This company, established in 1850, provided insurance against injuries emerging from railway and steamboat accidents.
